Molecular biology is the investigation of biological activity at a molecular level. It is also the study of biochemical reactions between molecules that happen in a cell. Molecular biology is essential since it can be applied to every single organism that exists, as all living organisms go through chemical reactions to control their composition. Some essential cellular components that may be familiar to you, such as DNA, membranes, and organelles, are all derived from simple reactions. Today we will look at quintessential components of molecular biology, including several macromolecules and different chemical reactions.
Carbon
Living organisms contain chemical substances, of which the majority contain carbon. These substances which include carbon are called organic compounds. However, one crucial point is that there are some exceptions, since carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, carbonates, and hydrogen carbonates contain carbon but are not considered as organic compounds.
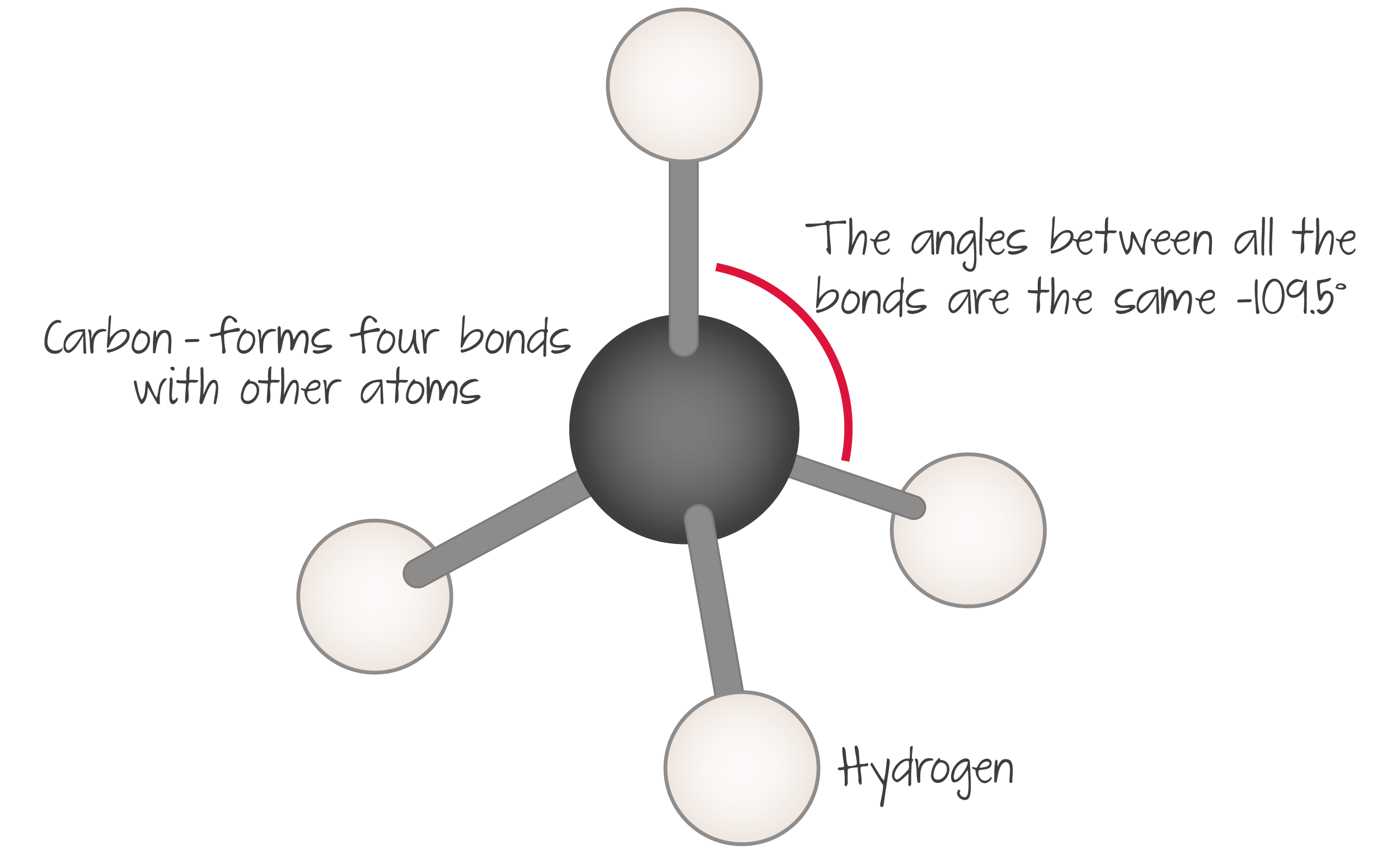
Carbon is an element that has 4 electrons in its outer shell. These electrons can form four covalent bonds with other elements including carbon. Consequently, there is a diversity of different carbon compounds since carbon can react with many other atoms and form arrangments. Some carbon compounds, like macromolecules, are composed of complex mechanisms such as chains or rings, whereas others, such as methane, are composed of four hydrogen atoms and one carbon atom.
Carbon Compounds
Living organisms are composed of carbon compounds, or macromolecules, which include carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. These four compounds all contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen atoms (O). It is important to know various types of macromolecules and their function.

Carbohydrates
- Alpha-D-glucose produces ATP in cells.
- Beta-D-glucose builds cell walls in plants.
- Starch is used as long-term storage in plants.
- Ribose is a component of RNA and DNA.
Lipids
- Triglycerides are used as long-term storage in animals.
- Steroids are chemical messengers in the body.
- Phospholipids compose plasma membranes.
Proteins
- Structural proteins form the structural framework of parts in the body.
- Enzymes speed up chemical reactions in the body by lowering the activation energy.
- Polypeptides make up a protein.
Nucleic Acids
- DNA stores genetic information.
- RNA creates proteins at ribosomes.
Chemical Reactions
Cell division, cell growth, and other cell activities are driven by chemical reactions. Here are the three critical terminologies that are useful to know:
- Metabolism – the totality of all enzymatic reactions
- Anabolism – the synthesis of complex molecules from simple molecules that require energy (ATP).
- Catabolism – the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler molecules that require hydrolysis and the release of energy
Works Cited
Allott, Andrew, and David Mindorff. Biology: Oxford IB Diploma Programme. Oxford University Press, 2014.
Leave a comment