Today I had my first class of internship at Samsung Medical Center. I learned some tools and tests that pathologists use while they work.
Frozen Section

Frozen section is a specific type of biopsy procedure developed to make a rapid diagnosis of a mass during surgery. Biopsies are small samples of tissue taken from a mass that is examined under the microscope for diagnosis. They are mostly used to figure out whether cancer cells are present or not, but sometimes other infections and diseases can be diagnosed as well. During the frozen section, the surgeon takes a part of the tissue mass, which is a biopsy. A pathologist takes the biopsy and freezes the tissue in a cryostat machine. He cuts the frozen tissue with a microtome and stains it with dyes so that it can be seen under the microscope. The frozen procedure usually takes only minutes.
There are several advantages of frozen section biopsy. First, if the pathologist needs more tissues for better diagnosis, the surgeon can obtain additional samples without having to operate again. The surgeons can proceed or stop the surgery because the pathologist can tell the surgeons whether the tissue is cancerous or not. Also through frozen section biopsy, the surgeon and pathologist can collaborate to better care for the patient.
When pathologists cannot make a diagnosis based on the frozen section, they must rely on the permanent section, a process in which the tissue is not frozen. Permanent section takes longer than a frozen section, but it leads to a higher quality of microscope slides.
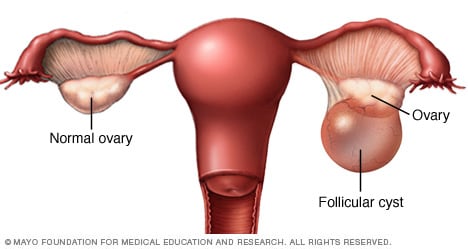
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs in the ovary. The two most common types of ovarian cysts are follicle cysts and corpus luteum cysts. Follicle cysts form when the follicle, a tiny sac in which an egg grows, does not break open to release the egg when the egg matures. Corpus luteum cysts form if the follicle sac does not shrink after releasing the egg. Most ovarian cysts, including follicle cysts and corpus luteum cysts, are benign (not cancerous). On the other hand, malignant (cancerous) cysts are rare and more common in older women.
The most common causes of ovarian cysts include endometriosis, pregnancy, and hormonal problems. Ovarian cysts usually don’t cause symptoms, but when it does, the pain often comes from the cyst rupturing or causing twisting of an ovary. Doctors most commonly used tests such as ultrasound, pregnancy test, blood test, and hormone level tests to plan treatments for ovarian cysts.
Multi-head Microscope

Multi head microscopes are commonly found in pathologists’ workplace. Through multi-head microscopes, many pathologists can look at the same microscope slide to make an accurate diagnosis. Multi-head microscopes are commonly found in pathologists’ workplace. Through multi-head microscopes, many pathologists can look at the same microscope slide to make an accurate diagnosis. Multi-head microscopes are also used to teach students. During class, students can see the slides and discuss what they think.
Echocardiogram
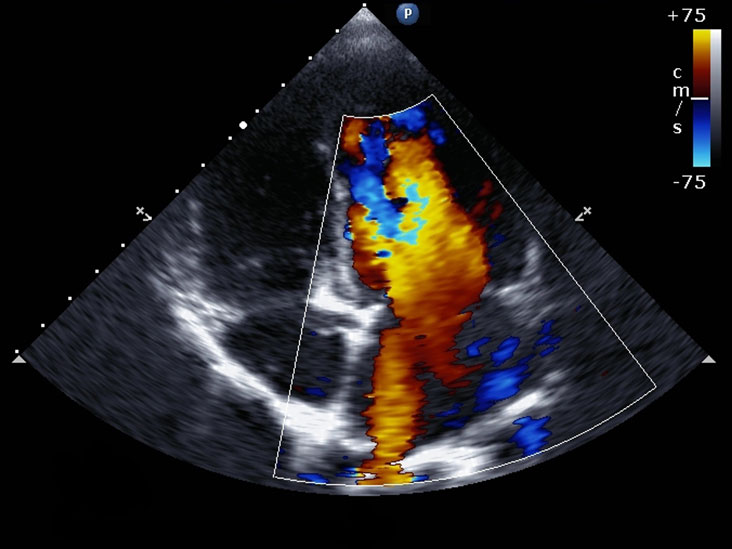
An echocardiogram is a test that uses high-frequency sound waves, also referred to as ultrasound, to take pictures of the heart. This test is also called diagnostic cardiac ultrasound or echocardiography. It can create images of the heart’s valves, walls, blood vessels, and chambers. When conducting this test, a transducer is passed over the patient’s chest. The transducer creates sound waves that bounce off the heart and echo back to the transducer. The waves that are echoed are changed into pictures.
An echocardiogram can help doctors determine whether the patient has any problems with the heart and whether the heart is functioning correctly. An echocardiogram is often used by doctors because there are no risks, and the doctor can actively see the heart moving.
Leave a comment